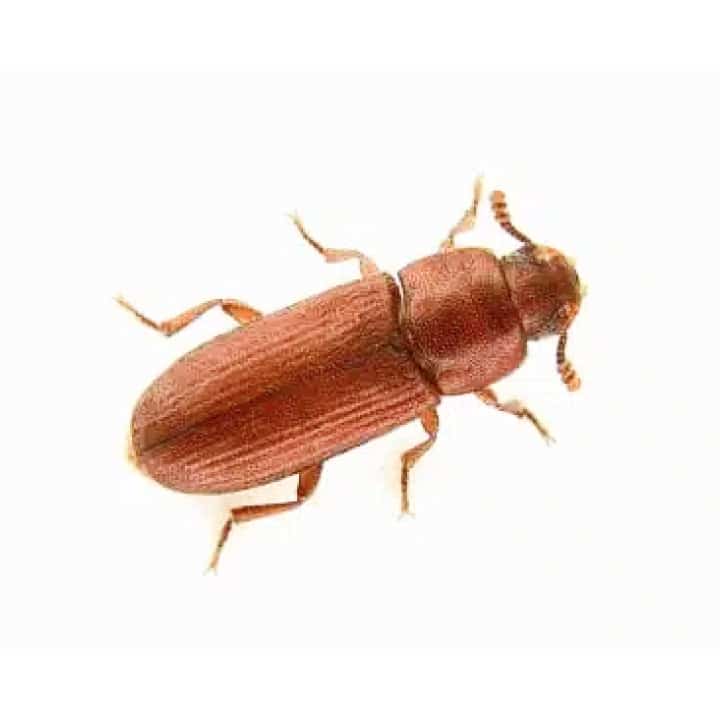
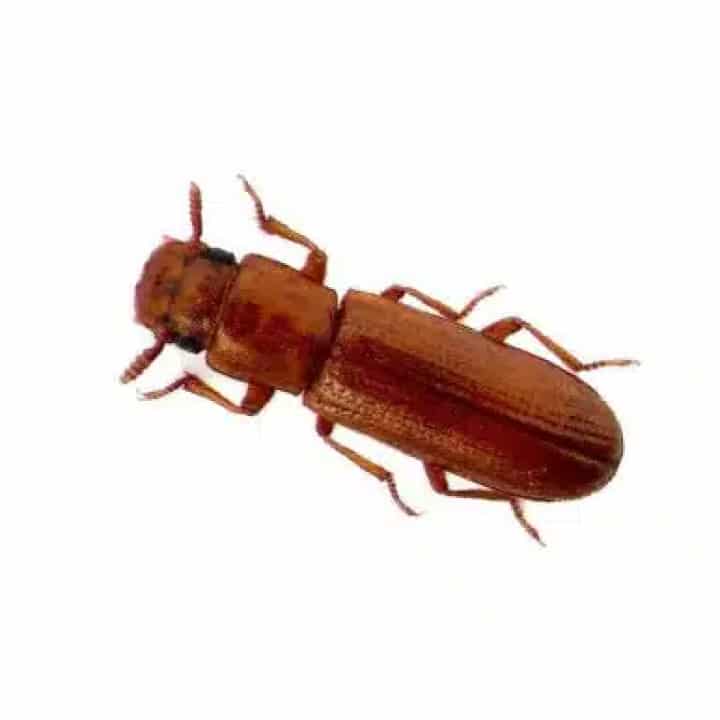
Habitat and Distribution – Rust-Red Flour Beetle (Tribolium castaneum)

Biology – Rust-Red Flour Beetle (Tribolium castaneum)
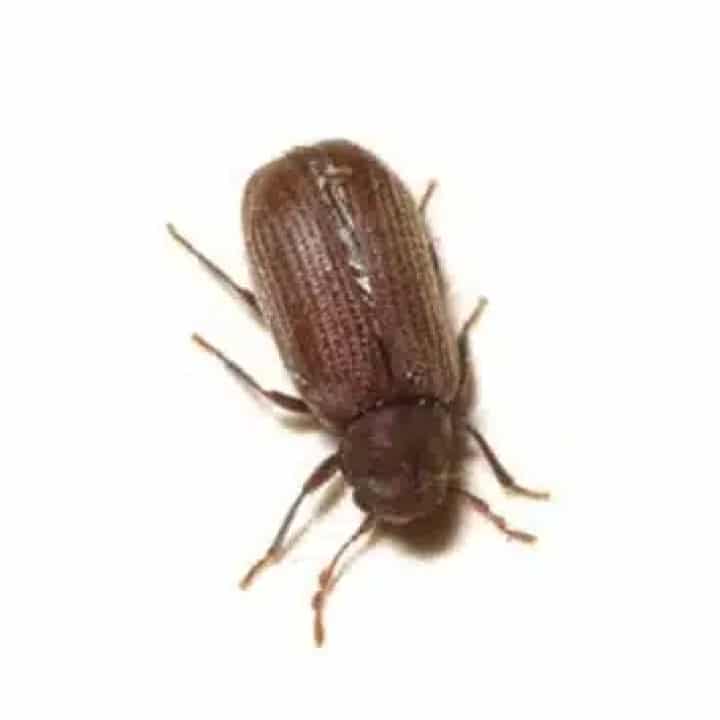
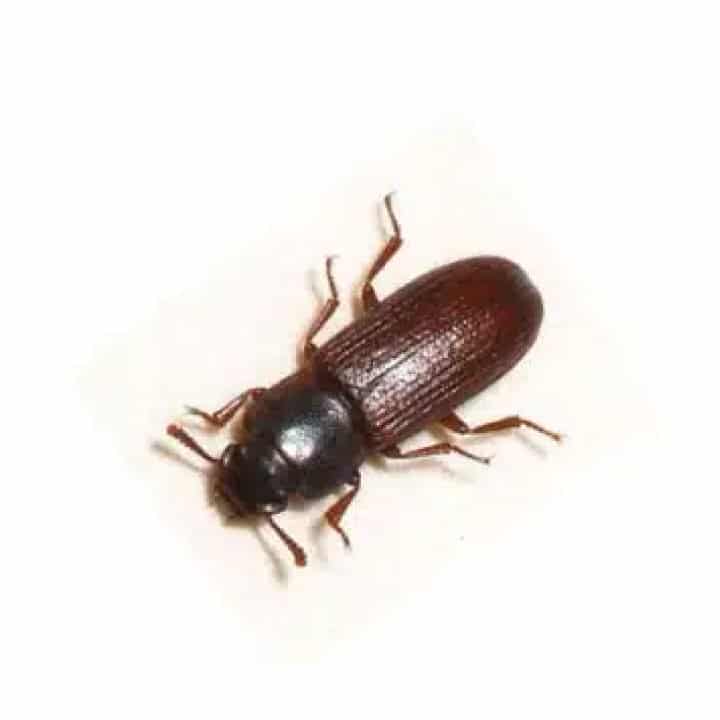
The Rust-Red Flour Beetle undergoes a complete metamorphosis with four life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
- Eggs: Each female can lay up to 450 eggs over several months. Eggs are laid directly onto larval food and typically hatch within one week.
- Larvae: Narrow and yellowish-white with faint banding, the larvae are free-living and feed openly in the infested material. They develop over 3 to 5 weeks.
- Pupae: Pupation occurs freely in the food material (not in a cocoon) and takes about 5 to 10 days.
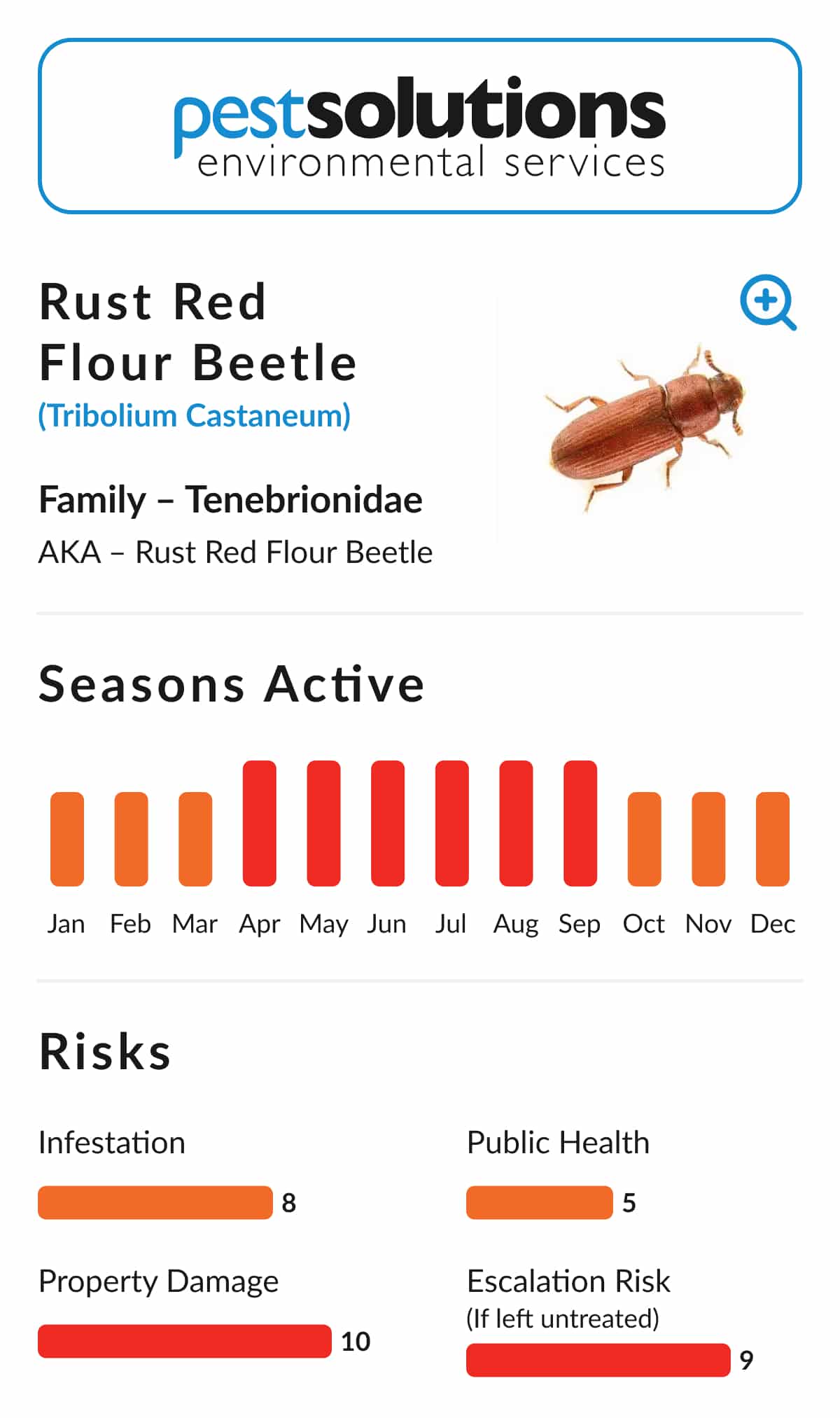
- Adults: Adults are 3–4 mm long with a shiny, rust-red appearance. They are often found grouped together due to an aggregation pheromone that attracts other beetles.
Under favourable conditions, the full life cycle can be completed in 1 to 2 months, making rapid population growth possible in warm environments.
Why They’re a Problem – Rust-Red Flour Beetle (Tribolium castaneum)
The Rust-Red Flour Beetle is a significant pest in flour and animal feed mills and is commonly introduced into facilities on imported commodities. Its presence leads to contamination, and it is known to taint flour and other products, resulting in product loss and hygiene concerns.
Although not considered a regular grain pest in the UK, this species can infest warm grain and may coexist with other stored product insects in temperature-controlled environments.
Control and Prevention – Rust-Red Flour Beetle (Tribolium castaneum)
Control of the Rust-Red Flour Beetle requires an integrated approach combining hygiene, monitoring, and insecticide application:
- Good hygiene: Clean machinery, floors, and storage areas to remove food residues and potential breeding sites.
- Monitoring: Use bait bags and pheromone traps to detect activity and assess the extent of infestations.
- Residual insecticides: Apply approved organophosphate or pyrethroid-based products to structural surfaces and processing areas.
- Fumigation: In the case of infested foodstuffs, fumigation by a licensed pest control specialist may be necessary to eliminate active beetle populations.
Prevention is key, especially in facilities processing flour and similar commodities where this beetle thrives.
Professional Support – Rust-Red Flour Beetle (Tribolium castaneum)
If you’re dealing with an infestation of Rust-Red Flour Beetles, early identification and treatment are essential to protect your food processing operations and avoid costly contamination.
Visit https://www.pestsolutions.co.uk to speak to our team or schedule a pest control inspection.